한국항공우주연구원
Mobile GnbCompact Advanced Satellite 500
Korea’s Cutting-Edge Satellites for Observing the Earth
Satellite
More countries are developing satellites, with more than 150 satellites launched each year worldwide. Earth observation satellites, meteorological/marine/environmental observation satellites, broadcasting/telecommunication satellites, and navigation satellites have an important role in national security and various fields such as economy, industry, and culture. The value of data observed from satellites is increasing as important big data in the 4th Industrial Revolution era.Securing satellite development technology to meet national public demand
The research and development of satellites in Korea began in 1994 when the General Science and Technology Council approved a multipurpose satellite (Arirang) development project. The multipurpose Arirang 1 was developed in 1999 to meet public demand for satellite images, with Arirang 2 developed under the initiative in Korea in 2006. Later, Arirang 3, Arirang 5, and Arirang 3A were developed in 2012, 2013, and 2015, respectively. Currently, KARI is developing Arirang 6, a high-precision radar satellite, and Arirang 7 and Arirang 7A as cutting-edge precision earth observation optical satellites. Moreover, it developed Cheollian 1, Korea’s first geostationary orbit satellite capable of independent meteorological and ocean observation services. It also developed—and is currently operating—Cheollian 2A, which is capable of more precise meteorological observation than Cheollian 1, and Cheollian 2B, which is capable of marine observation as well as the world’s first atmospheric environmental observation from the geostationary orbit. In particular, Cheollian 2B is expected to help resolve conflicts between countries and social problems due to fine dust by identifying the migration path of air pollutants, such as fine dust, around the Korean Peninsula. KARI has also developed small and scientific experimental satellites, such as Science and Technology 1 in 2003 and Naro Science and Science and Technology 3 in 2013. KARI has secured its independent satellite development technology by developing multipurpose satellites and geostationary orbit satellites. 500kg next-generation mid-size satellites 1 was launched in 2021 to transfer satellite technology to private industry with the aim of industrialising domestic satellites.| Subject | Arirang (Multipurpose Satellite) | Next-Generation Mid-Size Satellite | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 3A | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7A | 1 | 2 | |
| Purpose | Earth observation (Optical) | Precise earth observation (Optical) | Precise earth observation (Optical) | Precise earth observation (Optical + IR) | All-weather earth observation (Image radar) | All-weather earth observation (Image radar) | Precise earth observation (Optical + IR) | Precise earth observation (Optical + IR) | Earth observation (EOS) | Earth observation (EOS) |
| Satellite Shape |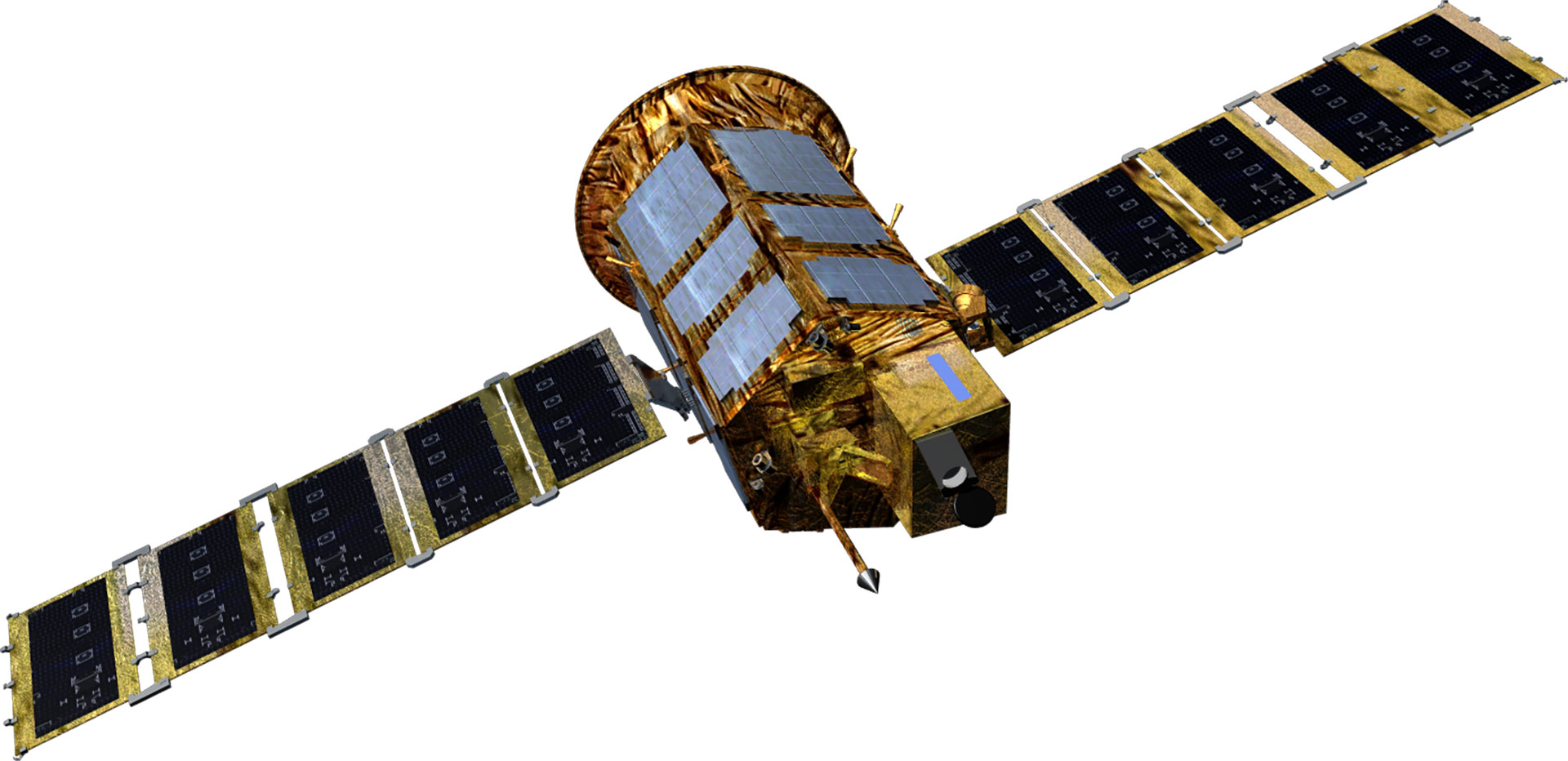  |
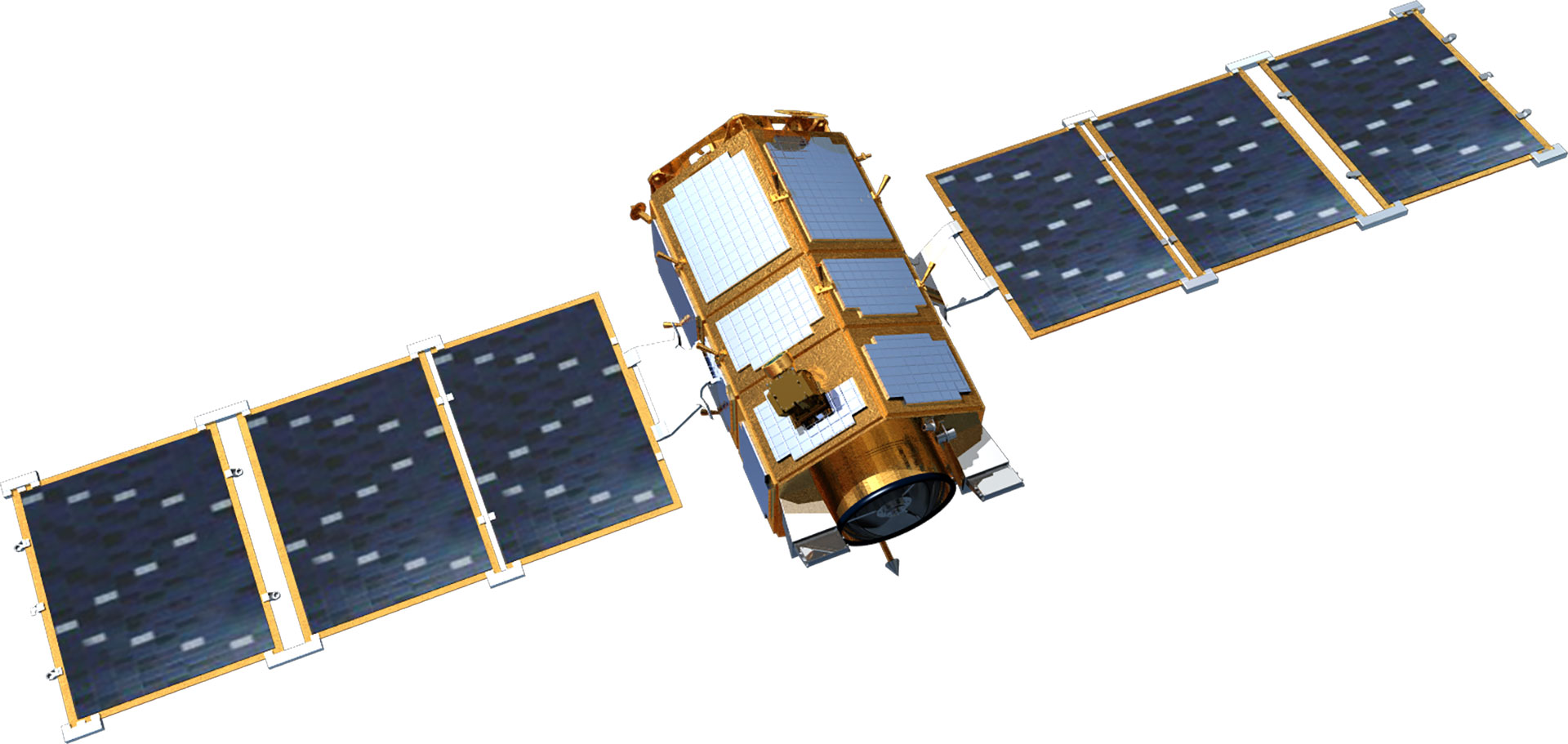 |
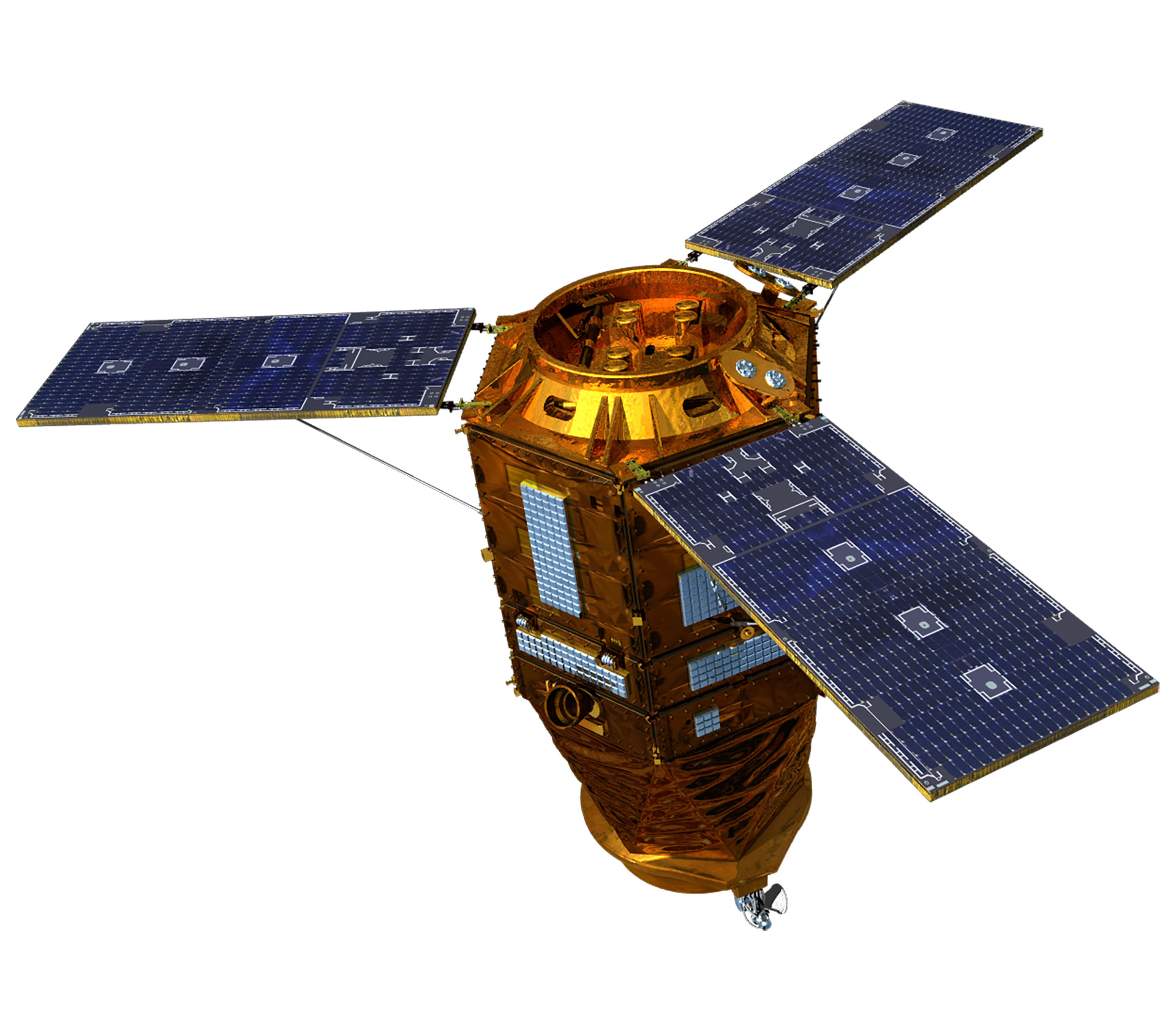 |
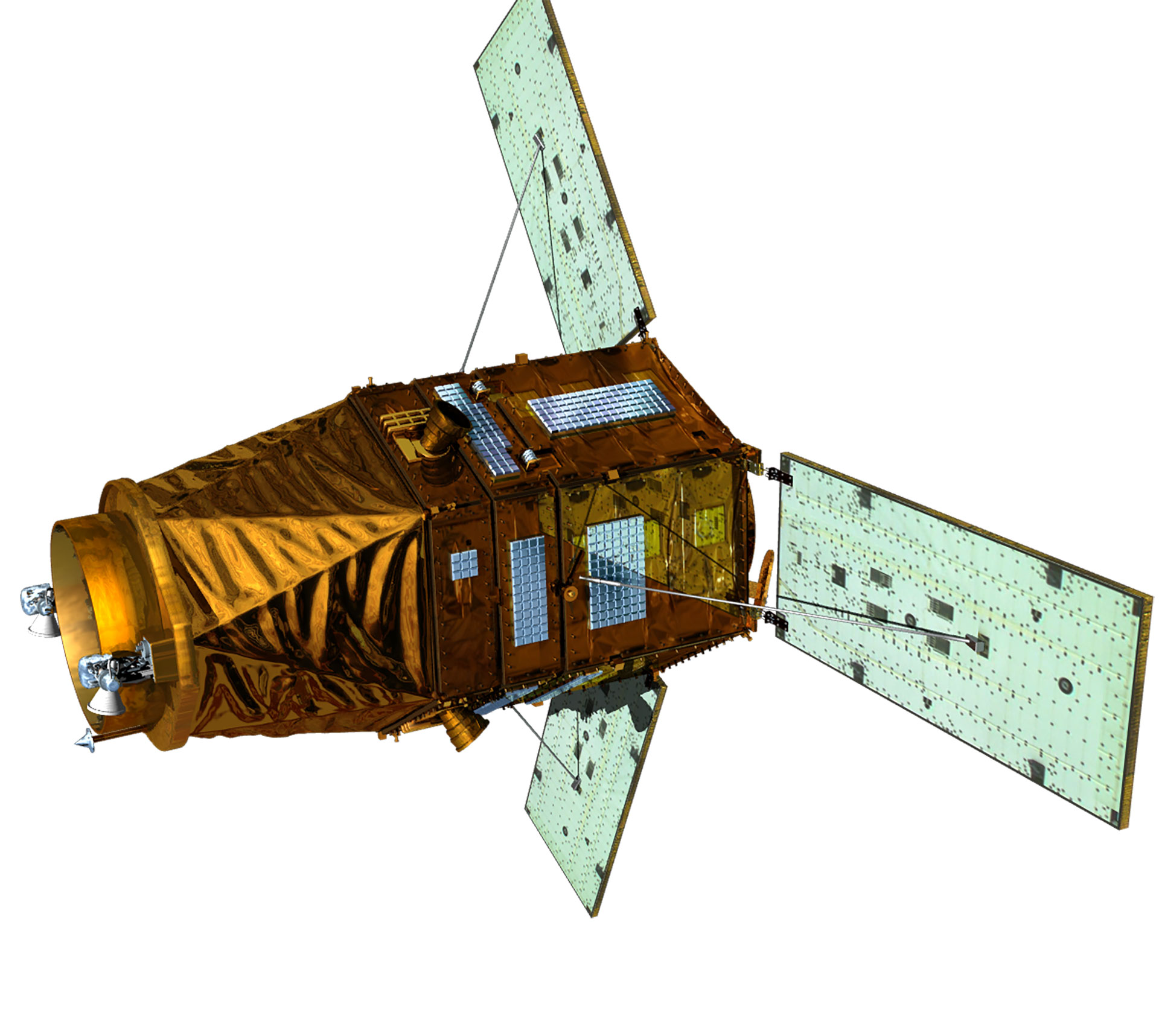 |
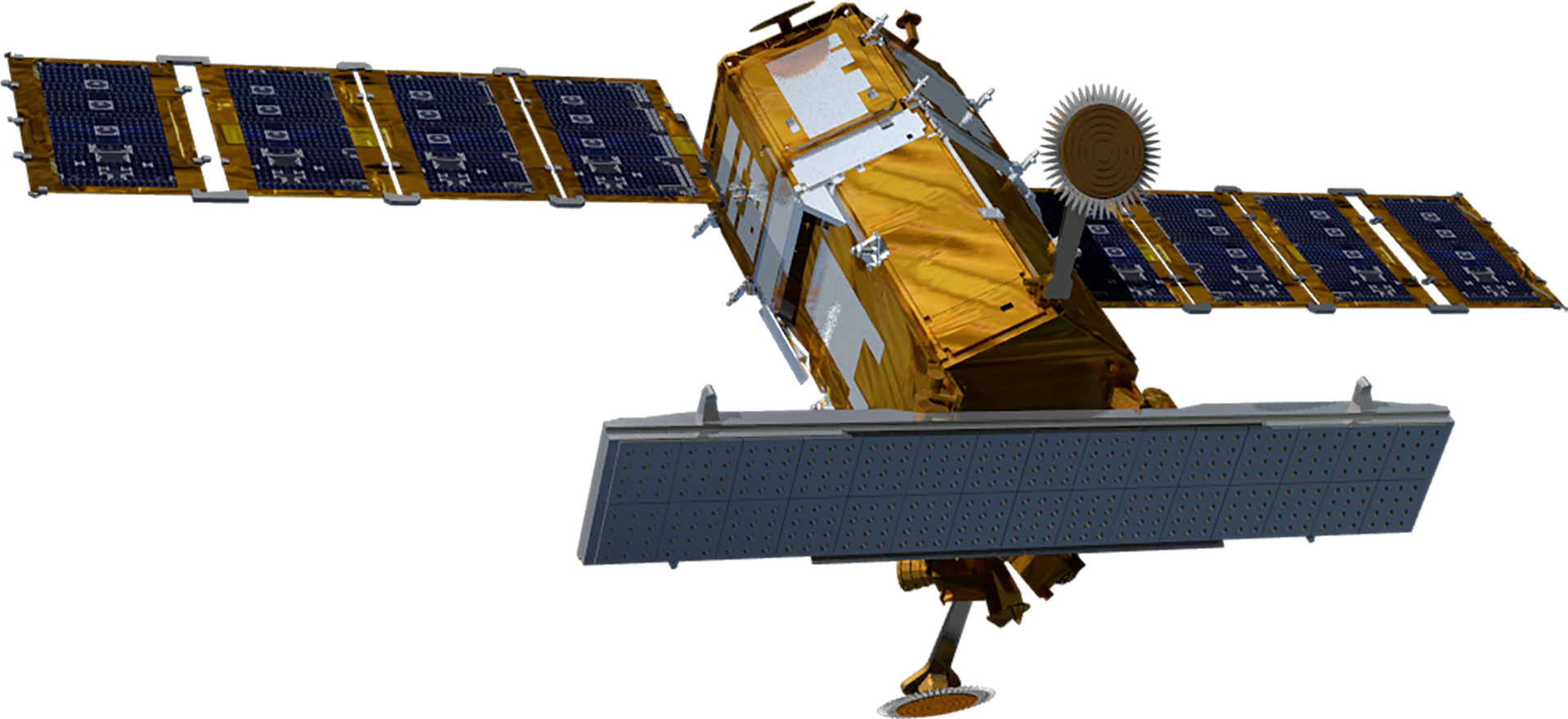 |
 |
 |
 |
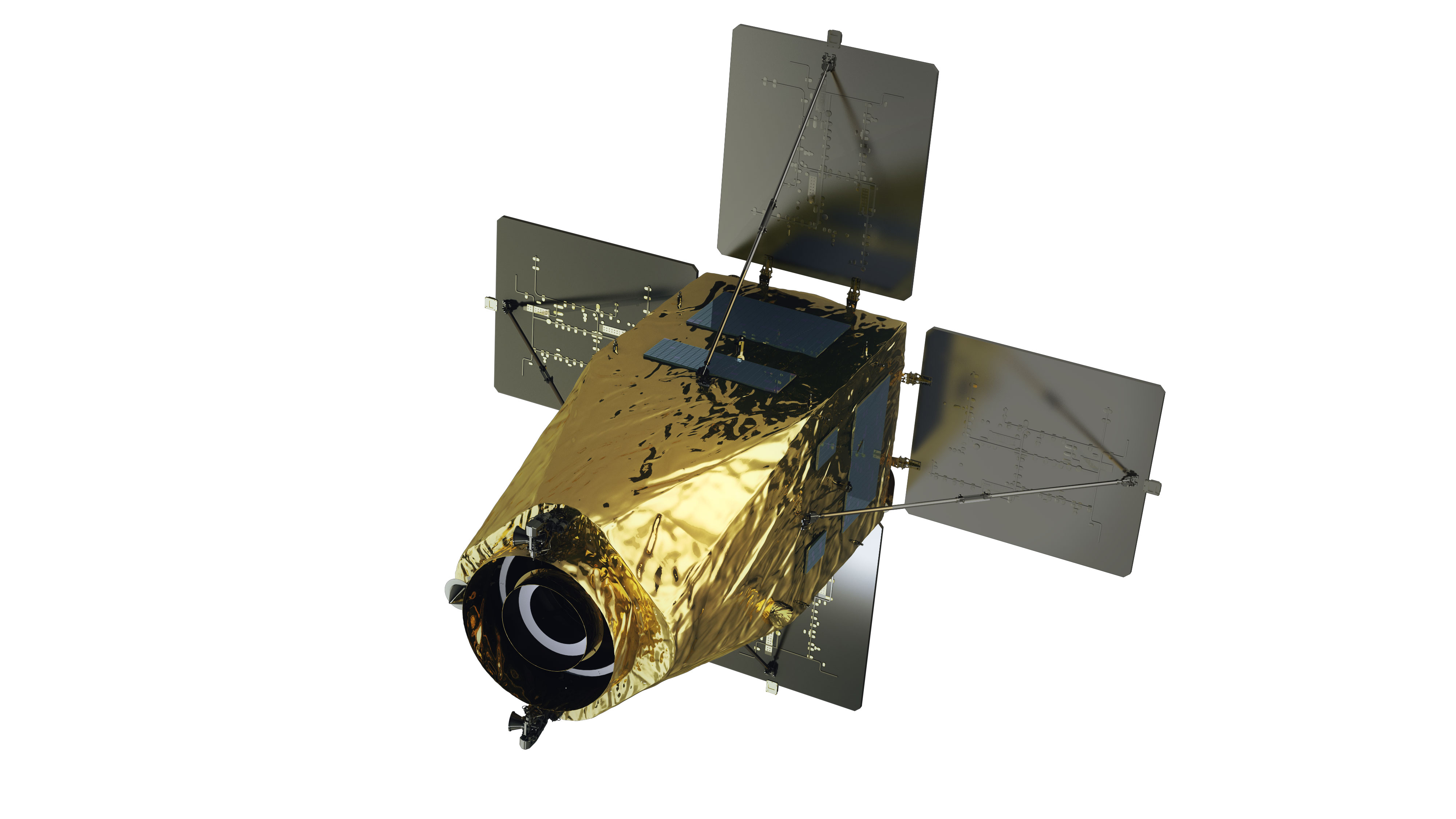 |
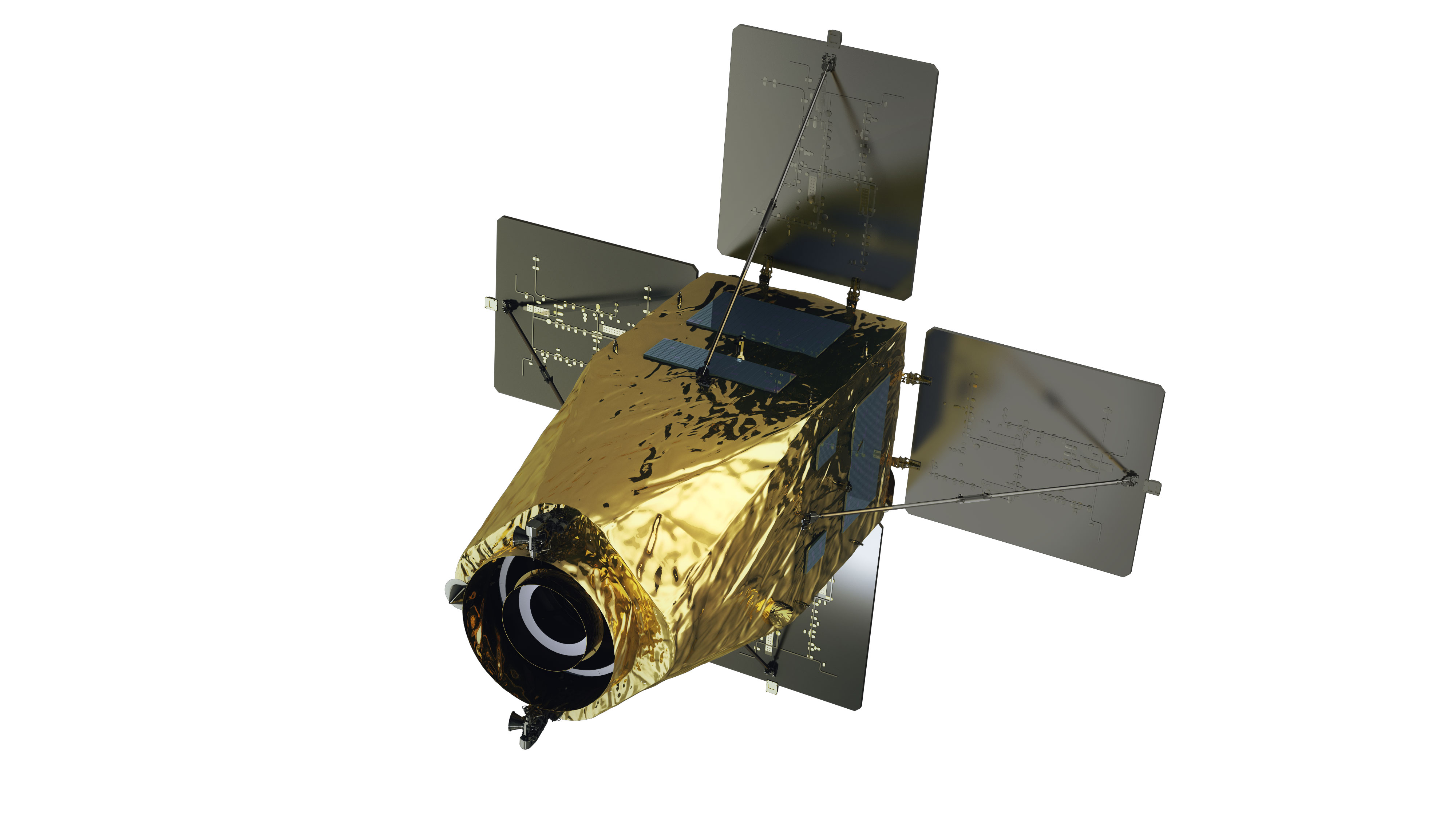 |
| Project Period | 1994.11- 2000.1 | 1999.12 - 2006.11 | 2004.8 - 2012.8 | 2006.12 - 2015.12 | 2005.6 - 2015.6 | 2012 - 2014 | 2016 - 2023 | 2016 - 2023 | 2015 - 2019 | 2018 - 2020 |
| Weight(kg) | 470 kg | 800 kg | 980 kg | Around 1,100 kg | Around 1,400 kg | 1,750 kg | 2000 kg | 2000 kg | 500 kg class | 500 kg class |
| Mission Life | 3 years | 3 years | 4 years | 4 years | 5 years | 5 years | 5 years | 5 years | 4 years | 4 years |
| Performance (resolution) |
B&W 6.6m | B&W 1m Color 4m |
B/W 0.7m Color 2.8m |
B&W 0.55m Color 2.2m |
Radar image 1m/3m/20m | Radar image 0.5m/3m/20m | B&W 0.3m Color 1.12m |
B&W 0.3, color < 1.12m | B&W 0.5m Color 2m |
B&W 0.5m Color 2m |
| Launch Vehicle | Taurus (US) | Rockot (Russia) | H2-A (Japan) | Dnepr (Russia) | Dnepr (Russia) | Vega-C (France) | Vega-C (France) | Falcon9(US) | Soyuz-2 (Russia) | - |
| Launch Site | Vandenberg (US) | Plesetsk (Russia) | Tanegashima (Japan) | Yasny (Russia) | Yasny (Russia) | Guyana (France) | Guyana (France) | Cape Canaveral(US) | Baikonur (Kazakhstan) | - |
| Launch Date | '1999.12.21 | '2006.7.28 | '2012.5.18 | '2015.3.26 | '2013.8.22 | To Be Determined | To Be Determined | To Be Determind | '2021.3.22 | To Be Determined |
| Operation Status | Mission completed (2007.12) | Mission completed (2015.10) | In operation | In operation | In operation | Under development | Under development | Under development | In operation | Under development |
| Type | Public geostationary orbital satellite | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheollian 1 | Cheollian 2A | Cheollian 2B | Cheollian 3 | |
| Purpose | Public communication/Marine/Weather observation | Weather/Spaceobservation | Marine/Environmentalobservation | Offering public satellite communication service |
| Shape |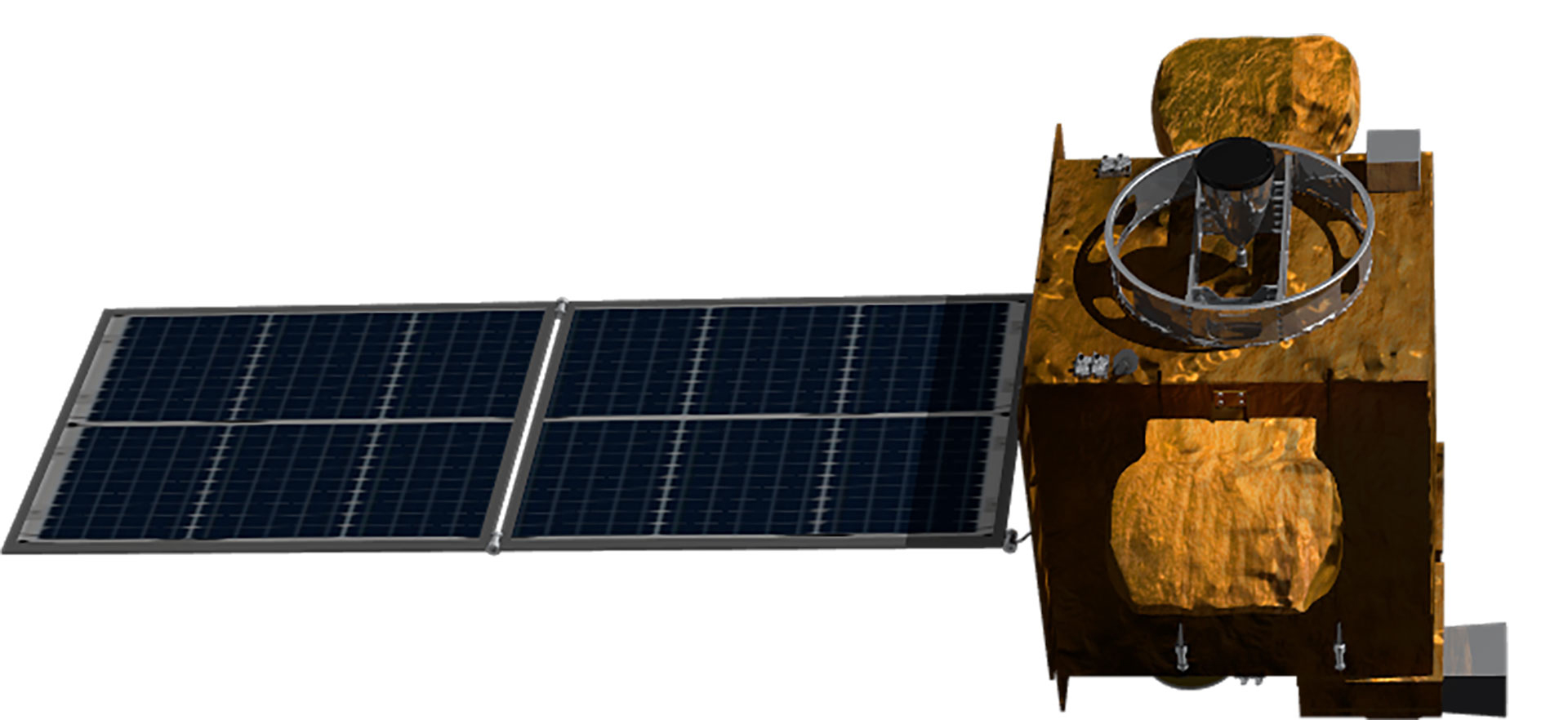  |
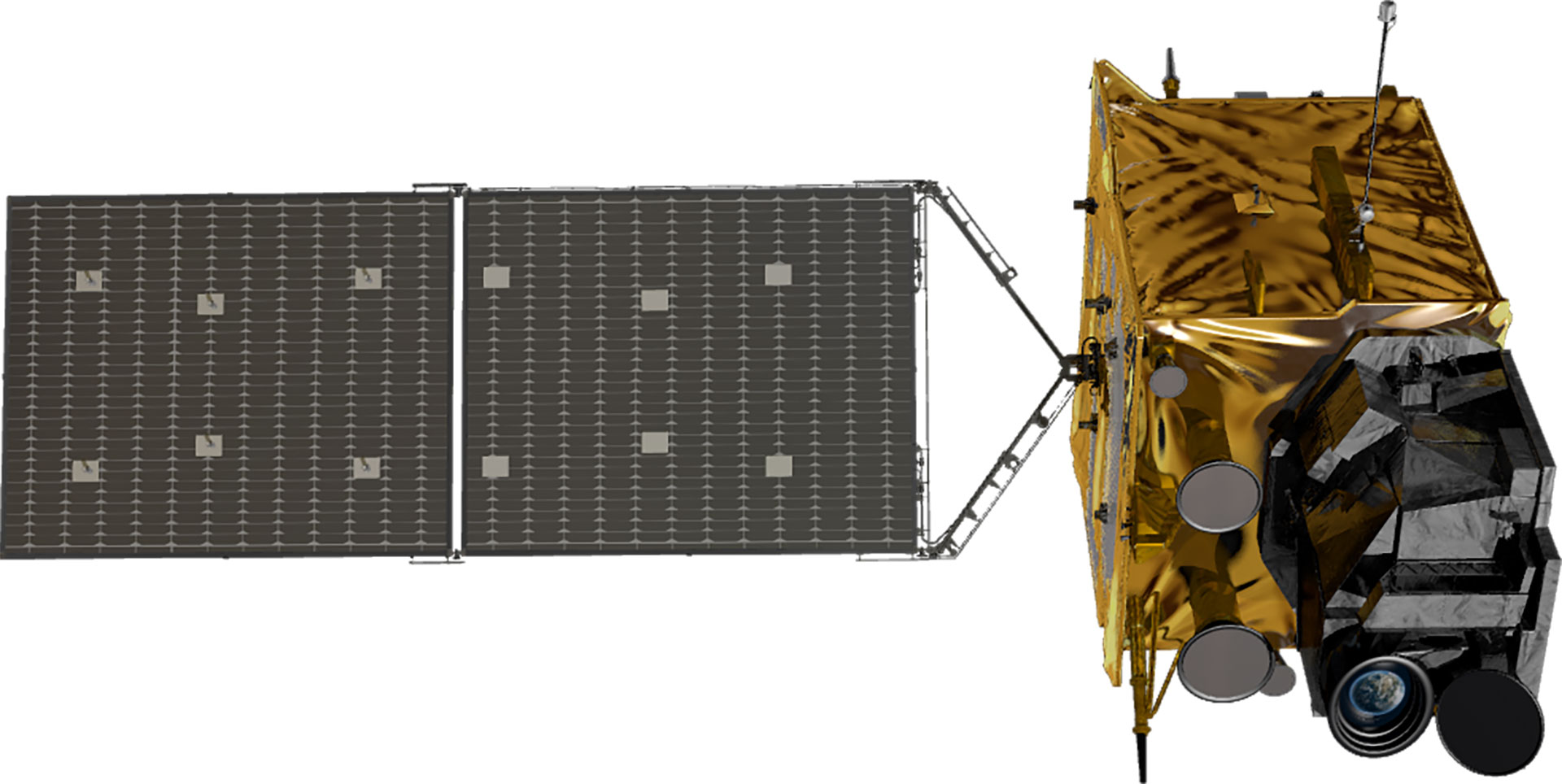 |
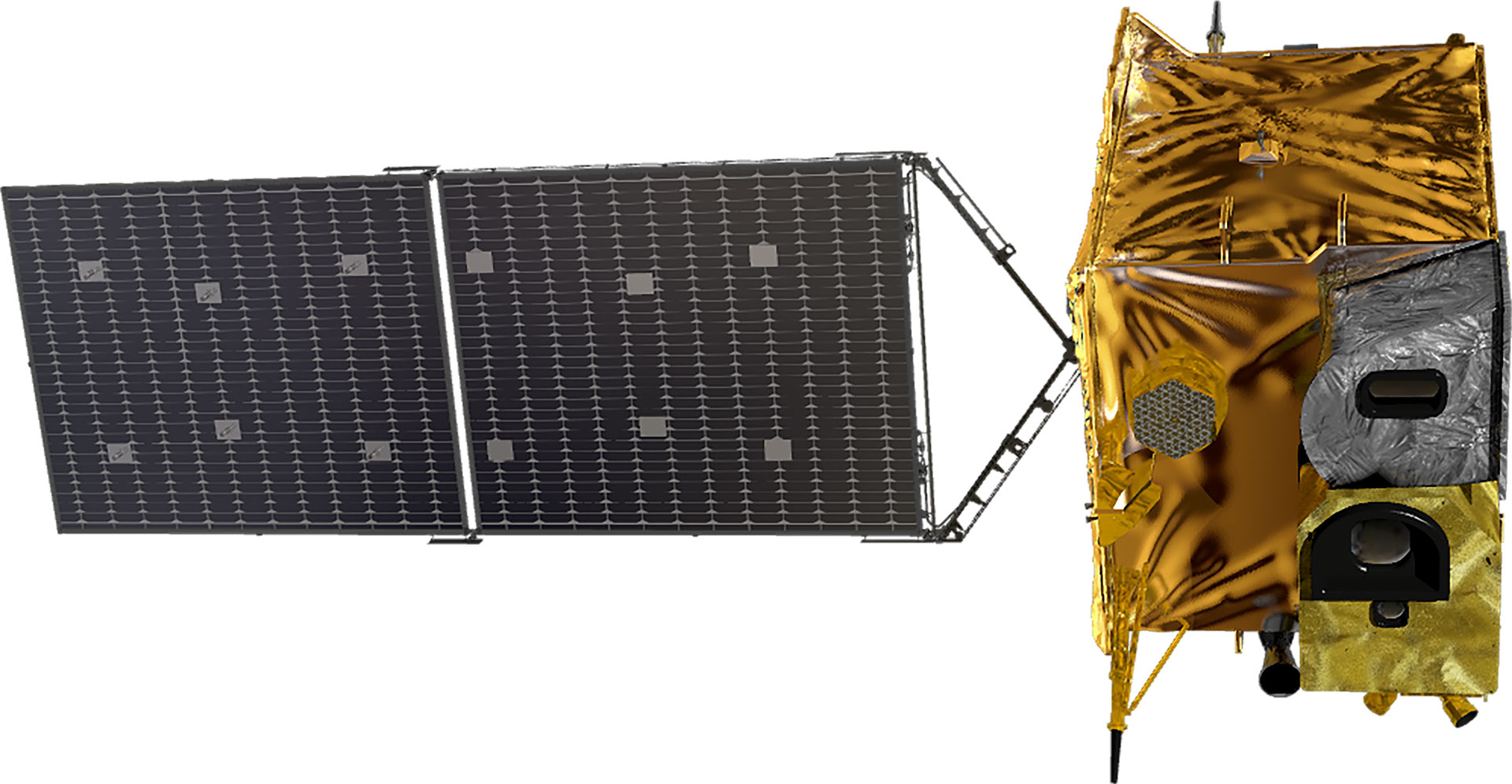 |
 |
| Development Period | 2003.9 - 2010.12 | 2011.7 - 2020.10 | 2021.4 - 2027.12 | |
| Launch Date | 2010.6.27 | 2018.12.5 | 2020.2.19 | To be Determined |
| Weight | 2,460 kg | 3,507 kg | 3,386 kg | 3,500 kg |
| Life | 7 years | 10 years | 10 years | 15 years |
| Satellite body development | Astrium(France)/KARIjoint development | KARI | KARI | KARI |
| Launch vehicle | Ariane5 (France) | Ariane5 (France) | Ariane5 (France) | - |
| Launch site | Guyana (France) | Guyana (France) | Guyana (France) | - |
| Remarks | Korea’s first geostationary orbital satellite | Geostationary orbital satellites independently developed in KOREA | ||
| Operation Status | Weather observation Mission completed (‘20.4.1) | In operation | In operation | Under development |
World-class satellite development technology
Although Korea was a latecomer, having begun developing satellites in the 1990s, it has come a long way thanks to continuous investment and R&D, and it is considered to be among the world's top six or seven in terms of satellite development capability. It has secured the world's most advanced satellite design, analysis, assembly, and test technologies to meet various domestic satellite demands. Having constructed a cutting-edge satellite testing facility, it owns satellite operation infrastructure and technology and satellite information utilization technology essential for satellite development. KARI has accumulated technologies for developing low-orbit earth observation satellites and geostationary satellites applying advanced technologies through world-class satellite research and development. It transfers its satellite development technologies to private industries.